Home Internet Services Cloud Solution
We are a team of seasoned cloud computing experts, who combine our expertise as consultants, strategists, and engineers.

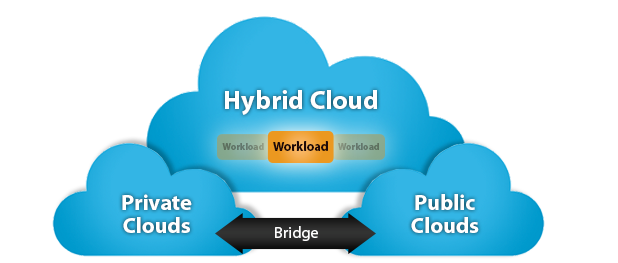
Who said it has to be all or nothing? You need your path to the cloud.
A flexible solution that changes as your needs change, is ideal. You don't have to choose—HPE GreenLake is the cloud that comes to you, your data centers, colos and edges. Choosing your own path to the cloud is hybrid cloud, wisely done.

Manage Cisco Catalyst infrastructure on-
prem or in the cloud.
Simplify, automate, secure, and unify experiences.
Discover software-enabled switching and wireless
management options that free up people and time.

Run operations in the cloud. Safely,
securely, and reliably.
Simplified, AI-powered monitoring and cloud IT operations
include templates, automation, and end-to-end
visibility. So you can see more and do more.
Modernize your on-premises infrastructure with fast and secured single-tenant private cloud, with the convenience of monthly billing for only the infrastructure use
Most cloud computing services fall into four broad categories: infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS),
serverless, and software as a service (SaaS). These are sometimes called the cloud computing "stack"
because they build on top of one another. Knowing what they are and how they’re different makes it easier to accomplish your business goals.
The most basic category of cloud computing services. With infrastructure as a service (IaaS), you rent IT infrastructure—servers and virtual machines (VMs), storage, networks, operating systems—from a cloud provider on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Platform as a service (PaaS) refers to cloud computing services that supply an on-demand environment for developing, testing, delivering, and managing software applications. PaaS is designed to make it easier for developers to quickly create web or mobile apps, without worrying about setting up or managing the underlying infrastructure of servers, storage, network, and databases needed for development.
Software as a service (SaaS) is a method for delivering software applications over the internet, on demand and typically on a subscription basis. With SaaS, cloud providers host and manage the software application and underlying infrastructure, and handle any maintenance, like software upgrades and security patching. Users connect to the application over the internet, usually with a web browser on their phone, tablet, or PC.
Overlapping with PaaS, serverless computing focuses on building app functionality without spending time continually managing the servers and infrastructure required to do so. The cloud provider handles the setup, capacity planning, and server management for you. Serverless architectures are highly scalable and event-driven, only using resources when a specific function or trigger occurs.
Simplify management of your containerized workloads in any client
environment with a pay-as-you-go model.
You’re probably using cloud computing right now, even if you don’t realize it. If you use an online service to send email, edit documents, watch movies or TV, listen to music, play games, or store pictures and other files, it’s likely that cloud computing is making it all possible behind the scenes. A variety of organizations—from tiny startups to global corporations, government agencies to non-profits—have embraced cloud computing technology for all sorts of reasons.
Quickly build, deploy, and scale applications—web, mobile, and API. Take advantage of cloud-native[RM1] technologies and approaches, such as containers, Kubernetes, microservices architecture, API-driven communication, and DevOps.
Reduce application development cost and time by using cloud infrastructures that can easily be scaled up or down.
Protect your data more cost-efficiently—and at massive scale—by transferring your data over the internet to an offsite cloud storage system that’s accessible from any location and any device.
Unify your data across teams, divisions, and locations in the cloud. Then use cloud services, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, to uncover insights for more informed decisions.
Connect with your audience anywhere, anytime, on any device with high-definition video and audio with global distribution.
Also known as software as a service (SaaS), on-demand software lets you offer the latest software versions and updates to customers—anytime they need, anywhere they are.
Use intelligent models to help engage customers and provide valuable insights from the data captured.
Cloud computing is a term used to describe the delivery of on-demand computing resources—hardware, storage, databases, networking, and software—to businesses and individuals via a network (usually the internet). Cloud computing enables organizations to access and store information without managing their own physical devices or IT infrastructure.
As the amount of data being generated and shared continues to increase and consumers demand more access to online services, it has become more difficult for companies to continue operating their businesses on in-house computing servers.
Platform as a service (PaaS): hardware and software resources needed for cloud application development
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS): on-demand access to compute, storage, networking, and virtualization
Similar to the way you check your email inbox online through a web browser, cloud computing enables companies to access and manage resources and applications anywhere there’s an internet connection.Cloud services are also typically managed and maintained by a third-party service provider, allowing IT teams to rapidly adjust compute and storage without having to pay upfront infrastructure costs or set up and manage yet more systems and applications.
You can choose public, private, or hybrid cloud deployments and the service model based on the level of flexibility, control,and management you need. The three main types of cloud service models include:
Software as a service (SaaS): full-application stack as a cloud service, including the maintenance and management from underlying infrastructure to application software
You can spin up new instances or retire them in seconds, allowing developers to accelerate development with quick deployments.Cloud computing supports new innovations by making it easy to test new ideas andV design new applications without hardware limitations or slow procurement processes.
Cloud computing gives your business more flexibility. You can quickly scale resources and storage up to meet business demands without having to invest in physical infrastructure.
Companies don’t need to pay for or build the infrastructure needed to support their highest load levels.Likewise, they can quickly scale down if resources aren’t being used.
Whatever cloud service model you choose, you only pay for the resources you actually use. This helps you avoid overbuilding and overprovisioning your data center and gives your IT teams back valuable time to focus on more strategic work.
Cloud storage enables you to make data available anywhere you are, anytime you need it. Instead of being tied to a location or specific device, people can access data from anywhere in the world from any device—as long as they have an internet connection.
Despite popular perceptions, cloud computing can actually strengthen your security posture because of the depth and breadth of security features, automatic maintenance, and centralized management.
Reputable cloud providers also hire top security experts and employ the most advanced solutions, providing more robust protection.
Cloud providers offer backup and disaster recovery features. Storing data in the cloud rather than locally can help prevent data loss in the event of an emergency, such as hardware malfunction, malicious threats, or even simple user error.